DESCRIPTION
Frequent description
The commercial exploitation of plant cell, tissue and organ cultures is now a actuality and the model new utilized sciences are already in place and creating shortly. Their emergence has provided new views and sharpened the principle focus of the strategies by which plant cell and tissue custom can help man. Together with the thrilling new developments in plant molecular biology, these in vitro procedures must allow plant bio technologists to ‘design’ crops and plant merchandise and exploit the whole industrial potential of plant cell cultures.
PROPERTIES
Top quality Stage
200
natural provide
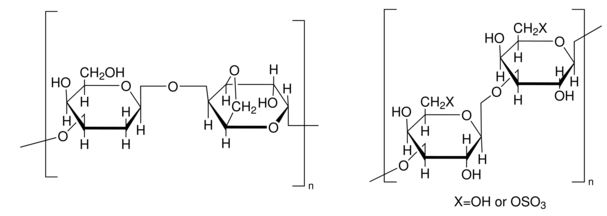
algae (Rhodophyceae)
sort
powder
utility(s)
cell custom | mammalian: acceptable
cell custom | plant: acceptable
microbiology: acceptable
transition temp
congealing temperature <38 °C (1.5% in H2O)
suitability
microbiology examined
Featured Enterprise
Agriculture
storage temp.
room temp
Utility
Agar has been used:
- as a reference commonplace industrial agar to match the physio-chemical, gelling properties of alkali-treated agar from Gracilaria tenuistipitata
- as an element inside the seed germination medium and rooting medium for commercially obtainable soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr) seeds
- as part of improvement media for B. subtilis mutant strain MTC871 based biofilm colonies
- as a bacteriological agar half to rearrange half energy Murashige-Skoog (MS 50%) medium for Echinocactus platycanthus seeds custom
PPM
Typical working focus: 6-12g/L.
Packaging
Biochem/physiol Actions
Completely different Notes
Bacterial Illnesses
Some micro organism inflicting infecting Cannabis crops embrace Pseudomonas syringae and Xanthomonas campestris pv. Cannabis. The indicators of Pseudomonas syringae are small water-soaked leaf spots which is able to enlarge alongside the veins, turning brown. The Xanthomonas campestris causes leaf spots and wilting in crops.
Fungal Illnesses
Just a few of the principle cannabis infecting fungus and illnesses attributable to them are:
- Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. Cannabis causes wilt whose indicators embrace yellowing of leaves, poor improvement, and wilt.
- Pythium sickness causes root rot and damping-off sickness whose indicators fluctuate from small roots lesions, excessive root damage, stunted improvement, to yellowing of leaves. Extra, damping-off impacts youthful seedlings.
- Sclerotinia sclerotiorum causes hemp canker whose preliminary indicators embrace watersoaked lesions on stalks and branches that will later set off cankers. Typically cottony white mycelium and black sclerotia could appear.
- Sphaeorotheca macularis or Leveillula taurica causes powdery mildew. It’s one of many essential widespread foliar illnesses of cannabis. Its indicators embrace powdery improvement on the ground of leaves that later turns brown.
- The cannabis plant will be affected by Alternaria species, which causes leaf spot and brown blight illnesses.
Viral and Viroid Illnesses
Viruses affecting cannabis embrace Hop mosaic virus (HpMV), Apple mosaic virus (ApMV), Hop stunt viroid (HSVd), Hop latent viroid, Arabis mosaic virus (ArMV), Alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV), Tobacco mosaic virus (TMC), Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV), and phytoplasmas.
The viruses could trigger excessive crop losses, reduce improvement, or impact the yield and prime quality of crops. The widespread indicators of viruses embrace yellow and inexperienced mosaic patterns on the leaves of Cannabis and curling, distortion, and narrowing of youthful leaves. Phytoplasmas primarily set off excessive shoot proliferation and stunted improvement.
 CD273 Antibody |
|||
| GWB-62C997 | GenWay Biotech | 0.2 mg | Ask for price |
 CD273 Antibody |
|||
| GWB-112DAB | GenWay Biotech | 0.1 mg | Ask for price |
 CD273 Antibody |
|||
| GWB-DF32E4 | GenWay Biotech | 0.1 mg | Ask for price |
 CD273 Antibody |
|||
| MBS8584207-01mL | MyBiosource | 0.1mL | EUR 305 |
 CD273 Antibody |
|||
| MBS8584207-01mLAF405L | MyBiosource | 0.1mL(AF405L) | EUR 465 |
 CD273 Antibody |
|||
| MBS8584207-01mLAF405S | MyBiosource | 0.1mL(AF405S) | EUR 465 |
 CD273 Antibody |
|||
| MBS8584207-01mLAF610 | MyBiosource | 0.1mL(AF610) | EUR 465 |
 CD273 Antibody |
|||
| MBS8584207-01mLAF635 | MyBiosource | 0.1mL(AF635) | EUR 465 |
 mAbConjugated Antibody) Mouse Anti-Human CD273 (PD-L2) mAbConjugated Antibody |
|||
| CCM031 | SAB | 100ul | EUR 476.4 |
 RAT ANTI MOUSE CD273 |
|||
| MBS214323-025mg | MyBiosource | 0.25mg | EUR 500 |
 RAT ANTI MOUSE CD273 |
|||
| MBS214323-5x025mg | MyBiosource | 5x0.25mg | EUR 2070 |
 mAb Conjugated Antibody) Mouse Anti-Human CD273 (PD-L2) mAb Conjugated Antibody |
|||
| MBS9455999-INQUIRE | MyBiosource | INQUIRE | Ask for price |
 Mouse Anti Human CD273 |
|||
| MBS225785-01mg | MyBiosource | 0.1mg | EUR 400 |
 Mouse Anti Human CD273 |
|||
| MBS225785-5x01mg | MyBiosource | 5x0.1mg | EUR 1630 |
) CD273 Antibody (RPE) |
|||
| GWB-1C4E00 | GenWay Biotech | 100 TESTS | Ask for price |
) CD273 Antibody (FITC) |
|||
| GWB-9413DB | GenWay Biotech | 0.1 mg | Ask for price |
 RAT ANTI MOUSE CD273:FITC |
|||
| MBS214325-01mg | MyBiosource | 0.1mg | EUR 435 |
 RAT ANTI MOUSE CD273:FITC |
|||
| MBS214325-5x01mg | MyBiosource | 5x0.1mg | EUR 1785 |
 Antibody) Mouse Monoclonal anti-Human CD273 (B7-DC, PD-L2) Antibody |
|||
| xAP-0206 | Angio Proteomie | 100ug | EUR 280 |
 Antibody) Mouse Monoclonal anti-Human CD273 (B7-DC, PD-L2) Antibody |
|||
| xAP-0207 | Angio Proteomie | 100ug | EUR 280 |
 CD273 Monoclonal Antibody |
|||
| E10-32031 | EnoGene | 100μg/100μl | EUR 225 |
|
Description: Available in various conjugation types. |
|||
 CD273 Monoclonal Antibody |
|||
| E10-32032 | EnoGene | 100μg/100μl | EUR 225 |
|
Description: Available in various conjugation types. |
|||



